Curtis Kingery, Lauren Powell, and Alex Upright (Advisor: Dr. Buchholz)

Background Information
“Genius Grant” award winner Angela Duckworth recently asked, “What is the single most significant choice a human being can make in their life?” Distinguished Psychology researcher David Buss responded, “The selection of a long-term mate.” Since he is esteemed for research in human mating, he might be biased to answer that way. However, it is undeniable that mating is a critical part of human existence. In mate selection, most traits and qualities are considered essential by both sexes (e.g., kind, trustworthy, intelligent), yet some traits are prioritized more by one sex than the other. These differences in preferences on traits most valued in an opposite-sex partner are well documented, along with an evolutionary rationale for their existence. On average, men disproportionately favor youthfulness and physical attractiveness in female mates. Women’s preferences show an asymmetry, on average, towards a man’s ability to acquire resources (Buss, 1989; Li et al., 2002; Walter et al., 2020). These traits may vary in one’s ability to control them. That is, there may be a significant difference between the ability to control one’s level of attractiveness versus the amount of control one has over their earning potential. Prior research on this topic found just that. Traits highly associated with female mate value are perceived as less controllable, by females, relative to traits highly associated with male mate value—and their perceived controllability by men (Ben Hamida et al., 1998). However, there is individual variation within the sexes on how they perceive their control over these traits. That is, males will vary in the extent to which they perceive control over characteristics suggestive of resource acquisition ability. We sought to account for these individual differences, generally, in perceived controllability of traits and, specifically, on critical mating dimensions. (Mis)perceptions of control could inform our understanding of documented differences in human behavior between males and females.
Methods
Participants were recruited from a pool of current students attending Roanoke College through the College’s Psychology department SONA system, primarily students enrolled in PSYC 101 or INQ260-PY who were eligible for extra credit received a half-credit as compensation for the participation. There were 26 male participants and 69 female participants, for a total of 95 participants who completed the study.
Our survey was administered using Qualtrics where participants were asked to respond to a variety of different scales, including the Locus of Control, the Scale for Intrasexual Competition (specified for either male or female, depending on the participant’s indicated gender) and a controllability questionnaire. Participants in the manipulation group were shown eight images, one of a person’s body ‘before’ working out and getting fit, and the second of the same person’s body ‘after’ working out. This particular manipulation was used in order to explore the possibility of intervention where countermessaging could increase people’s perceptions of control of traits that they wish to improve. Participants were also asked demographic questions such as gender identity and sexual orientation.
Results and Discussion
We expected to find a relationship between one’s level of intrasexual competitiveness and their perceived controllability of myriad traits. Although the relationship wasn’t strong enough to make any reliable conclusions, we did see a reduction in perceived controllability as participants, on average, increased in intrasexual competitiveness. See figure 1.
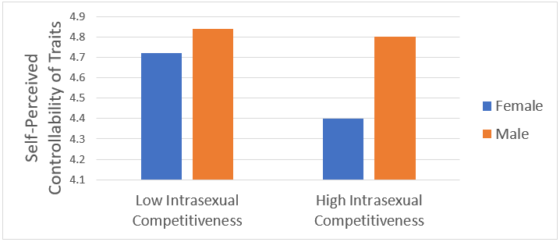
Figure 1: The effect of intrasexual competitiveness and sex on self-perceived controllability
Figure 1 implies that as one focuses more on competing with same-sex peers for mates, their perceptions of control over their traits could be influenced by that preoccupation.
Similarly, we expected our experimental manipulation, where half of the participants saw body transformation images, to increase that group’s average perception of controllability. We did not find evidence for this relationship. This could mean that our manipulation wasn’t strong enough or it could imply that perceptions of controllability may be stable traits within individuals that are unlikely to be influenced in this manner.
As predicted, we did find that males and females, on average, showed substantial differences in their general perceptions of controllability of traits. See figure 2.
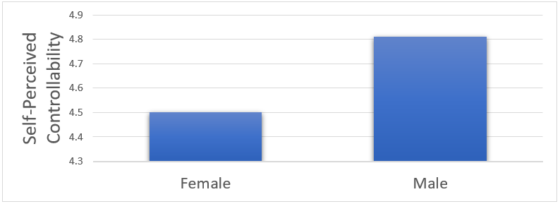
Figure 2: Self-perceived controllability of traits by sex
Moreover, we found a statistically significant result for differences in males’ and females’ perceptions of controllability, specifically on the dimensions regarded as critical to men when choosing a female mate. That is, traits related to youthfulness and attractiveness were considered more controllable by men than women. There was no evidence for these sex differences on perceptions of controllability for resource acquisition traits. These sex differences in perceptions of controllability could inform our understanding of behaviors that show increased or decreased occurrence in one sex versus the other (e.g., mate preferences, risk-taking, aggression, jealousy, and several psychological disorders such as depression and eating disorders).
Reflection
Unfortunately, while we were unable to find a strong enough relationship between competitiveness and controllability to make any conclusions, we were still able to determine a statistically significant difference in males’ and females’ perception of how well they can control their youthfulness and attractiveness.
Conclusion
We are all different people with different experiences and lives. There is no need to stress unnecessarily about being as attractive or successful as possible for fear of missing out on the perfect spouse. There is no need to compare yourself to others or feel that you must complete with them to find “the perfect mate.” Be patient, focus on the things that will not be changed by time, such as humor or personality, and make sure that you can be the best you can be, and the right person will be there at the right time.
References
Ben Hamida, S., Mineka, S., & Bailey, J. M. (1998). Sex differences in perceived controllability of mate value: An evolutionary perspective. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75(4), 953–966. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.75.4.953
Buss, D. M. (1989). Sex differences in human mate preferences: Evolutionary hypotheses tested in 37 cultures. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 12, 1–14. doi:10.1017/ S0140525X00023992
Li, N. P., Bailey, J. M., Kenrick, D. T., & Linsenmeier, J. A. W. (2002). The necessities and luxuries of mate preferences: Testing the tradeoffs. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 82(6), 947–955. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.82.6.947
Walter, K. V., Conroy-Beam, D., Buss, D. M., Asao, K., Sorokowska, A., Sorokowski, P., Aavik, T., Akello, G., Alhabahba, M. M., Alm, C., Amjad, N., Anjum, A., Atama, C. S., Atamtürk Duyar, D., Ayebare, R., Batres, C., Bendixen, M., Bensafia, A., Bizumic, B., … Zupančič, M. (2020). Sex differences in mate preferences across 45 countries: A large-scale replication. Psychological Science, 31(4), 408–423. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797620904154