Rachel Harmon, Emily Jones, Carter Smith, Shannon Blair Snyder, Kayleigh Walker
(Advisor: Dr. Findley-Van Nostrand)

Background Information
There have been many studies conducted on attachment styles (i.e., characteristic ways of emotionally connecting with others) between parents and their children, and studies performed to evaluate romantic relationship satisfaction, but there are few studies combining the two concepts in young adults (Xia et al., 2018). Attachment style is developed through an individual internalizing their relationship, or lack thereof, with a primary caregiver in infancy and early childhood (Searle & Meara, 1999). We wanted to look at whether attachment style is associated with emerging adults’ current romantic relationship satisfaction. We also explored additional variables such as gender and length of the relationship. We chose to focus on individuals in emerging adulthood for several reasons. First, it is during this formative stage individuals are considering life-changing decisions regarding education, friendships, careers, and romantic relationships (Arnett, 2000). Second, romantic relationships in this stage differ from those experienced in adolescence because they tend to be longer in duration and more serious in intention (Arnett, 2000). Finally, little research has been done on emerging adults’ romantic relationships and our research can provide insight into this newly defined developmental stage.
Methods
Participants in our study were students from Roanoke College who were at least 18 years old and in a committed romantic relationship. Participants for this study were recruited through the Roanoke College Psychology Department via SONA, as well as within the greater campus community. Participants who were enrolled in a psychology course received a half SONA credit for participating. Eighty-five total participants completed the study.
Our study was an online survey through Qualtrics. Participants were asked to answer questions regarding gender, gender of their partner, their sexuality, age, relationship length, whether they and their significant other have “taken a break” and if so, the number of “breaks” they’ve taken. To measure attachment style, we used the 36-item Experiences in Close Relationships-Revised Questionnaire. Scores on the ECR-R were calculated to reflect overall attachment insecurity, and anxious- and avoidant-attachment security as subscales. For relationship satisfaction, we used the 32-item Couple Satisfaction Index.
Results and Discussion
As expected, participants with secure attachment style reported higher relationship satisfaction (see Figure below- low scores on the ECR-R indicate more secure attachment). Also as expected, attachment-related anxiousness and attachment-related avoidance explained a pretty large amount of relationship satisfaction. Contrary to expectations, the association between attachment style and relationship satisfaction was stronger for participants who identified as male compared to participants who identified as female. Additionally, participants who reported higher levels of attachment-related anxiety and attachment-related avoidance had been in their current romantic relationship for a shorter-duration compared to participants with secure attachment. However, participants who had been with their current romantic partner for a longer amount of time reported higher levels of romantic relationship satisfaction. Participants who had not previously broken up with their current romantic partner also recorded significantly higher levels of relationship satisfaction compared to those who had previously broken up or “taken a break”.
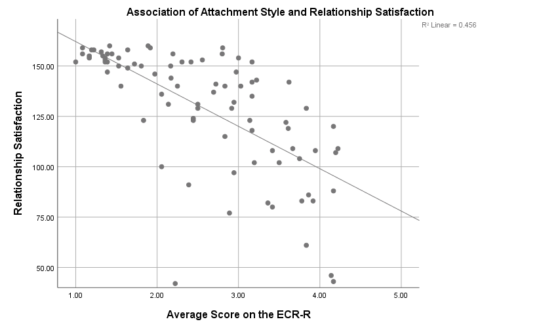
Romantic relationships are an important part of emerging adulthood (Arnett, 2000). The results of the current study indicate that attachment style may influence satisfaction within romantic relationships during this phase of development. The results expand upon previous literature by investigating these associations specifically in emerging adulthood, while exploring the additional factors of gender, relationship duration and whether couples had previously broken up or “taken a break”.
Reflection
This research process has been one that challenged us all in various ways throughout the semester. The first obstacle we faced was developing a study that interested us all and was relevant to the course. Our original goal with this study was to have the Roanoke College student and their significant other complete the survey in person. Requiring both the SONA student and their significant other to complete an in-person questionnaire limited our pool of students to those in relationships with a peer and those in a relationship with someone who is local. This meant that students who are in long distance relationships, and who may have had a lot to offer the research, were unable to partake in it. The original goal with having both individuals in a relationship complete the survey was to be able examine relationship satisfaction and attachment style within a relationship.
We originally decided to make this an in-person survey to increase validity. However, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and the transition to remote learning, our study had to be switched to online only. With this new requirement of the study having to be online, we had to re-evaluate our methods. We changed the study requirement of both partners needing to complete it, to only surveying one partner. This increased the number of students who could participate in our study, which we believe improved our sample size. Conducting the study online may have eliminated any response bias that would have occurred in the lab because originally they would have been taking the survey across from their significant other, and may have felt pressure or guilt to respond a certain way, which could have altered their initial thoughts or feelings. Overall, working remotely on this has been challenging and time consuming. Having to completely rethink our study methods and then communicate with one another via WIFI when two group members have poor connection was difficult. We no longer had the option to meet whenever was convenient and work on the data analyses as a group. We instead had to find time where we could all video chat and then have one person screen share, running analyses, while the others watched. In the end, switching to online research was beneficial because we were able to broaden our pool of participants, adjust our research in an efficient way, and find significant associations.
Conclusion
The main finding of our study indicates that the attachment style is associated with romantic relationship satisfaction. It is important to remember that attachment styles begin forming soon after birth and continue to evolve through the lifespan (Searle & Meara, 1999). While attachment-related anxiety and attachment-related avoidance were found to be significantly associated with romantic relationship satisfaction, we were also able to conclude that male romantic relationship satisfaction is somewhat more likely to be dependent upon attachment style in comparison to females.
References
Arnett, J. J. (2000). Emerging adulthood: A theory of development from the late teens through the twenties. American Psychologist, 55(5), 469-480.https://doi.org/10. 1037/0003-066X.55.5.469
Searle, B., & Meara, N. M. (1999). Affective dimensions of attachment styles: Exploring self-reported attachment style, gender, and emotional experience among college students. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 46(2), 147–158. https://doi.org/10. 1037/0022-0167.46.2.147
Xia, M., Fosco, G., Lippold, M., & Feinberg, M. (2018). A developmental perspective on young adult romantic relationships: Examining family and individual factors in adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 47(7), 1499-1516. doi:10.1007/s10964-018-0815-8